Welcome to Guangdong LINA Machinery Co.,Ltd. Official website
Welcome to Guangdong LINA Machinery Co.,Ltd. Official website
Product
News
RealName:Mr. Wang
Mobile:18027008185
Email:lina_paul@linajx.com
CompleteAddress:LINA Tech Park,Cai Yun East Road Houjie town Dongguan Guangdong
The working principle of the open mill:
Think about a few questions
Why can the open mill transform high elasticity raw rubber into plastic rubber with plasticity?
The use of an open mill for plasticizing mainly involves the shearing and squeezing action of two relatively rotating rollers on the rubber material, which breaks the original macromolecular chains of the rubber material, thereby reducing its elasticity and increasing its plasticity, which is beneficial for the subsequent processing steps.
The currently used plasticizing methods are mainly the roll forming plasticizing method and the thin pass plasticizing method.
2. How to mix the rubber material evenly with various additives?
The open mill mainly relies on two relatively rotating rollers to produce squeezing and shearing effects on the rubber material during the rubber mixing process. After multiple kneading and the accompanying chemical reactions during the kneading process, the large molecular chains inside the rubber are broken, and the various components in the formula are mixed evenly, ultimately achieving the purpose of rubber mixing. The film discharged from the gap between the rollers is wrapped around one roller due to the difference in surface speed and temperature between the two rollers, and then returns to the gap between the two rollers. This process repeats multiple times to complete the rubber mixing process. Promote the molecular chain of rubber to shorten and the elasticity to decrease during plasticization; During the mixing process, the surface of each component of the rubber material is continuously updated and uniformly mixed. On the intermittent operation of the open mill, the rubber material is repeatedly passed through the roller spacing several times after feeding, and finally cut into pieces.
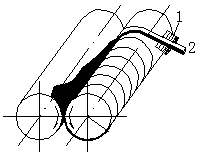
Intermittent rubber mixing process diagram
1- Addition 2- Pinching 3- Cutting of rubber material
On an open mill used for continuous operation, the rubber material is continuously added from one end of the roller, repeatedly passed through the roller several times according to the specified time of the rubber mixing process, and the required rubber strip is continuously cut from the other end of the roller. As shown in the figure.
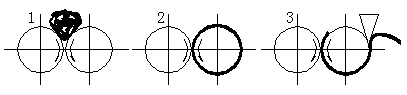
Continuous rubber mixing process diagram
1- Rubber cutting knife 2- Belt shaped rubber strip
3: What conditions should be met to achieve good rubber mixing effect when processing rubber materials on an open mill?
We will discuss from two aspects, namely from the perspectives of mechanics and rheology.
A、 Study the conditions for rubber material to enter the roller distance from a mechanical perspective
During the rubber mixing operation, we can see that when the rubber material is wrapped around a roller, there is still a certain amount of accumulated rubber between the two rollers. These accumulated rubber are continuously carried into the roller gap by the rotating rollers, and new accumulated rubber is constantly formed. These stacked adhesives have a significant impact on the rubber mixing effect.
If there is too much accumulation, the excess adhesive cannot enter the roller gap in time and can only be gently shaken in place, resulting in a significant decrease in the rubber mixing effect.
If there is too little accumulated glue, stable and continuous operation cannot be formed.
It can be seen that it is necessary to determine the appropriate amount of stacking adhesive, and for this, a concept called contact angle needs to be introduced.
The so-called contact angle refers to the angle between the contact point a of the rubber material on the roller and the line connecting the center of the roller section and the horizontal line of the center line of the roller section, expressed as α. As shown in the figure.
Whether the rubber material can enter the roller gap depends on the friction coefficient and contact angle between the rubber material and the roller.
Taking the rubber material as the research object and the contact point a as the edge research point, during the rubber mixing process, the rubber material exerts a radial force (resultant force) on the roller, that is, transverse pressure, represented by P. Conversely, according to the relationship between the force and the reaction force, the roller exerts an equal and opposite force on the rubber material, that is, the reaction force of transverse pressure, represented by F. Decompose this force into a horizontal force Fx and a tangential force Ft.
The function of Fx is to exert compression on the rubber material and cause it to deform;
The function of Ft is to push the rubber material out of the roller distance
。
In addition, there is friction between the rubber material and the roller during the movement process, that is, there is frictional force. The frictional force of the rubber material on the roller is represented by T ', and the direction deviates from the roller distance. On the contrary, the friction force of the roller on the rubber material, represented by T, enters the roller distance in the direction, and its function is to pull the rubber material into the roller distance.
If you want the rubber material to enter the roller spacing for rubber mixing, only
T>Ft
T - is the frictional force, which should be T=F ·μ, F is the positive pressure, and μ is the coefficient of friction; μ=tg φ, where φ is the friction angle.
∴T=F·tgφ
From the graph, it can be seen that Δ FtFA indicates that
Ft=F · tg α α is the contact angle of the adhesive material
T>Ft again
There is T=F · tg φ>Ft=F · tg α
That is, TG φ>TG α
∴ Has a diameter greater than α
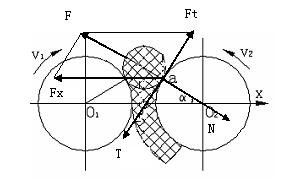
From the analysis, it can be seen that only when the friction angle φ is greater than the contact angle α, can the rubber material enter the roller distance.
Only when this condition is met can normal rubber mixing be guaranteed. The friction angle between rubber or rubber material and metal roller is related to the composition and formula of the rubber material, plasticity, mixing temperature, and surface shape of the roller. Φ=38~420, The friction angle between raw rubber and metal roller is φ=38041 ', and the contact angle α=32-400 is generally used during the rubber mixing process. It is recommended to use α=36-400 in China.
B: Mainly studied from a rheological perspective
1. How is the squeezing effect of rubber material generated? And its relationship with lateral pressure? The rubber material undergoes strong compression and shear in the roller gap, as shown in the figure. The squeezing effect is caused by the rubber material passing through gradually decreasing roller spacing, and the squeezing force increases with the increase of lateral pressure.
2. How is the shearing effect of adhesive produced? And who is related to the magnitude of shear force?
The shearing effect is caused by the speed ratio between the front and rear rollers, and the larger the speed ratio, the greater the shearing force.
3. Does the size of the roller spacing affect the shear effect of the rubber material and the rubber mixing effect?
For the same machine, the speed ratio and roller line speed are constant, and the method of reducing the roller distance can be used to increase the speed gradient, thereby increasing the shear effect on the rubber material. This is the principle behind the thin plastic molding of raw rubber. A large velocity gradient value results in good rubber mixing effect, especially for breaking and plasticizing effects. But when the energy required for shear deformation of the rubber material increases, the temperature of the rubber material rises, so it is necessary to strengthen cooling.
4. Why do we need to cut and flip the rubber during the rubber mixing process?
During the rubber mixing process, cutting the rubber material is crucial for the process. According to the analysis of fluid mechanics, the streamline distribution of the rubber material during the rubber mixing process is shown in the figure.

From the figure, it can be seen that the streamline of the rubber material near the roller is parallel to the rotating surface of the roller. At the beginning of the wedge-shaped section, there is a reflux area that forms two closed reflux lines (i.e., the ψ -0 line). When v1=v2, these two closed reflux lines are symmetrically distributed, and when v1, the neutral planes of the two closed reflux lines move towards the slow roller side. It can be seen that when v1=v2, the shear effect on the closed reflux line is smaller than that of v1, which affects the effectiveness of rubber mixing. So, most rubber mixing machines are designed with two rollers with different speeds (v1 ≠ v2).
However, even with different speeds, the optimal rubber mixing effect cannot be achieved. This is because when v1 ≠ v2, the wedge-shaped rubber strip still has closed reflux. Only by using the method of cutting rubber strips can the rubber material move along the axis of the roller, continuously breaking the reflux and accelerating the rubber mixing process, achieving good results.
The rubber material is subjected to strong compression and shear in the roller gap. The squeezing effect is caused by the rubber material passing through gradually decreasing roller spacing, and the squeezing force increases with the increase of lateral pressure; The shearing effect is caused by the speed ratio between the front and rear rollers, and the larger the speed ratio, the greater the shearing force.
For the same machine, the speed ratio and roller line speed are constant, and the method of reducing the roller distance can be used to increase the speed gradient, thereby increasing the shear effect on the rubber material. This is the principle behind the thin plastic molding of raw rubber. A large velocity gradient value results in good rubber mixing effect, especially for breaking and plasticizing effects. But as the energy required for shear deformation of the adhesive increases, the temperature of the adhesive rises rapidly, so it is necessary to strengthen cooling.
C: To enhance the rubber mixing effect, four conditions must be met
After the above analysis and discussion, it can be concluded that in order to complete the rubber mixing operation and achieve better rubber mixing results, the following four points should be achieved:
1. Make the friction angle of the rubber material greater than the contact angle (φ>α) in order to bring the rubber material into the roller spacing;
2. Make the front and rear roller speeds (line speeds) unequal in order to exert strong compression and shear on the rubber material in the roller gap;
3. When mixing rubber, it is necessary to cut and flip the rubber to break the closed reflux line of the rubber material and enhance the dispersion effect of the material;
4. During the rubber mixing process, the roller spacing is continuously adjusted to change the speed gradient and improve the rubber mixing effect.
—

Contacts:Mr. Wang

Mobile:18027008185


Email:lina_paul@linajx.com
Address:LINA Tech Park,Cai Yun East Road Houjie town Dongguan Guangdong


Official Accounts

Mobile website